Transect tutorial
4 minute read
This is a demonstration script for using the Transect class in the COAsT
package. This object has strict data formatting requirements, which are
outlined in tranect.py.
Transect subsetting (a vertical slice of data between two coordinates): Creating them and performing some custom diagnostics with them.
In this tutorial we take a look at subsetting the model data along a transect (a custom straight line) and creating some bespoke diagnostics along it. We look at:
1. Creating a TRANSECT object, defined between two points.
2. Plotting data along a transect.
3. Calculating flow normal to the transect
Import relevant packages
import coast
import matplotlib.pyplot as plt
/usr/share/miniconda/envs/coast/lib/python3.10/site-packages/pydap/lib.py:5: DeprecationWarning: pkg_resources is deprecated as an API. See https://setuptools.pypa.io/en/latest/pkg_resources.html
/usr/share/miniconda/envs/coast/lib/python3.10/site-packages/pkg_resources/__init__.py:2871: DeprecationWarning: Deprecated call to `pkg_resources.declare_namespace('pydap')`.
Implementing implicit namespace packages (as specified in PEP 420) is preferred to `pkg_resources.declare_namespace`. See https://setuptools.pypa.io/en/latest/references/keywords.html#keyword-namespace-packages
/usr/share/miniconda/envs/coast/lib/python3.10/site-packages/pkg_resources/__init__.py:2871: DeprecationWarning: Deprecated call to `pkg_resources.declare_namespace('pydap.responses')`.
Implementing implicit namespace packages (as specified in PEP 420) is preferred to `pkg_resources.declare_namespace`. See https://setuptools.pypa.io/en/latest/references/keywords.html#keyword-namespace-packages
/usr/share/miniconda/envs/coast/lib/python3.10/site-packages/pkg_resources/__init__.py:2350: DeprecationWarning: Deprecated call to `pkg_resources.declare_namespace('pydap')`.
Implementing implicit namespace packages (as specified in PEP 420) is preferred to `pkg_resources.declare_namespace`. See https://setuptools.pypa.io/en/latest/references/keywords.html#keyword-namespace-packages
/usr/share/miniconda/envs/coast/lib/python3.10/site-packages/pkg_resources/__init__.py:2871: DeprecationWarning: Deprecated call to `pkg_resources.declare_namespace('pydap.handlers')`.
Implementing implicit namespace packages (as specified in PEP 420) is preferred to `pkg_resources.declare_namespace`. See https://setuptools.pypa.io/en/latest/references/keywords.html#keyword-namespace-packages
/usr/share/miniconda/envs/coast/lib/python3.10/site-packages/pkg_resources/__init__.py:2350: DeprecationWarning: Deprecated call to `pkg_resources.declare_namespace('pydap')`.
Implementing implicit namespace packages (as specified in PEP 420) is preferred to `pkg_resources.declare_namespace`. See https://setuptools.pypa.io/en/latest/references/keywords.html#keyword-namespace-packages
/usr/share/miniconda/envs/coast/lib/python3.10/site-packages/pkg_resources/__init__.py:2871: DeprecationWarning: Deprecated call to `pkg_resources.declare_namespace('pydap.tests')`.
Implementing implicit namespace packages (as specified in PEP 420) is preferred to `pkg_resources.declare_namespace`. See https://setuptools.pypa.io/en/latest/references/keywords.html#keyword-namespace-packages
/usr/share/miniconda/envs/coast/lib/python3.10/site-packages/pkg_resources/__init__.py:2350: DeprecationWarning: Deprecated call to `pkg_resources.declare_namespace('pydap')`.
Implementing implicit namespace packages (as specified in PEP 420) is preferred to `pkg_resources.declare_namespace`. See https://setuptools.pypa.io/en/latest/references/keywords.html#keyword-namespace-packages
/usr/share/miniconda/envs/coast/lib/python3.10/site-packages/pkg_resources/__init__.py:2871: DeprecationWarning: Deprecated call to `pkg_resources.declare_namespace('sphinxcontrib')`.
Implementing implicit namespace packages (as specified in PEP 420) is preferred to `pkg_resources.declare_namespace`. See https://setuptools.pypa.io/en/latest/references/keywords.html#keyword-namespace-packages
Define filepaths for data and configuration
root = "./"
# And by defining some file paths
dn_files = root + "./example_files/"
fn_nemo_dat_t = dn_files + "nemo_data_T_grid.nc"
fn_nemo_dat_u = dn_files + "nemo_data_U_grid.nc"
fn_nemo_dat_v = dn_files + "nemo_data_V_grid.nc"
fn_nemo_dom = dn_files + "coast_example_nemo_domain.nc"
# Configuration files describing the data files
fn_config_t_grid = root + "./config/example_nemo_grid_t.json"
fn_config_f_grid = root + "./config/example_nemo_grid_f.json"
fn_config_u_grid = root + "./config/example_nemo_grid_u.json"
fn_config_v_grid = root + "./config/example_nemo_grid_v.json"
Load data variables that are on the NEMO t-grid
nemo_t = coast.Gridded(fn_data=fn_nemo_dat_t, fn_domain=fn_nemo_dom, config=fn_config_t_grid)
Now create a transect using the coast.TransectT object.
The transect is between the points (54 N 15 W) and (56 N, 12 W). This needs to be passed the corresponding NEMO object and transect end points. The model points closest to these coordinates will be selected as the transect end points.
tran_t = coast.TransectT(nemo_t, (54, -15), (56, -12))
# Inspect the data
#tran_t.data # uncomment to print data object summary
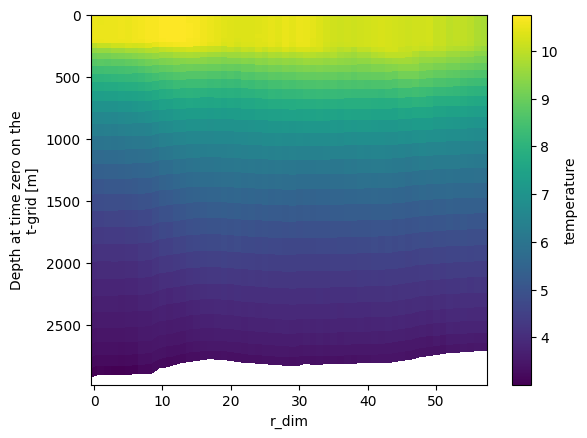
Plot the data
# It is simple to plot a scalar such as temperature along the transect:
temp_mean = tran_t.data.temperature.mean(dim="t_dim")
plt.figure()
temp_mean.plot.pcolormesh(y="depth_0", yincrease=False)
plt.show()
Create a nemo f-grid object
With NEMO’s staggered grid, the first step is to define the transect on the f-grid so that the velocity components are between f-points. We do not need any model data on the f-grid, just the grid information, so create a nemo f-grid object
nemo_f = coast.Gridded(fn_domain=fn_nemo_dom, config=fn_config_f_grid)
Transect on the f-grid
tran_f = coast.TransectF(nemo_f, (54, -15), (56, -12))
# Inspect the data
#tran_f.data # uncomment to print data object summary
Load model data on the u- and v- grids
nemo_u = coast.Gridded(fn_data=fn_nemo_dat_u, fn_domain=fn_nemo_dom, config=fn_config_u_grid)
nemo_v = coast.Gridded(fn_data=fn_nemo_dat_v, fn_domain=fn_nemo_dom, config=fn_config_v_grid)
Calculate the flow across the transect
tran_f.calc_flow_across_transect(nemo_u, nemo_v)
# The flow across the transect is stored in a new dataset where the variables are all defined at the points between f-points.
#tran_f.data_cross_tran_flow # uncomment to print data object summary
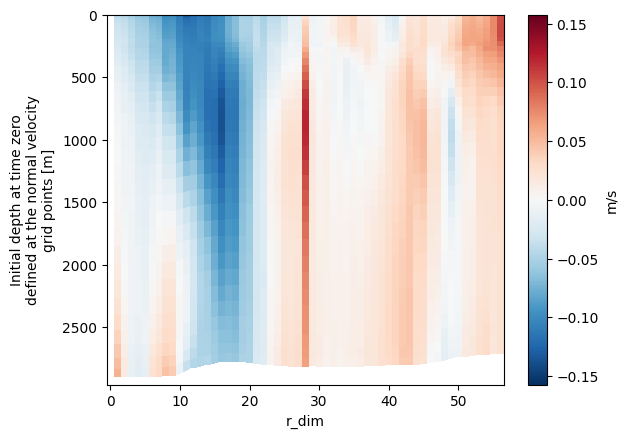
Plot the time averaged velocity across the transect
# To do this we can plot the ‘normal_velocities’ variable.
cross_velocity_mean = tran_f.data_cross_tran_flow.normal_velocities.mean(dim="t_dim")
plt.figure()
cross_velocity_mean.rolling(r_dim=2).mean().plot.pcolormesh(yincrease=False, y="depth_0", cbar_kwargs={"label": "m/s"})
plt.show()
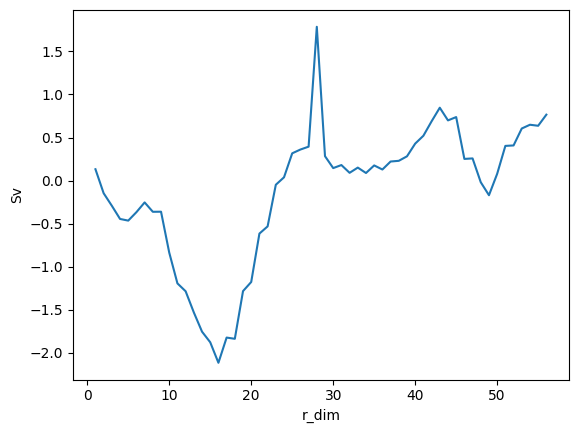
Plot volume transport across the transect
# To do this we can plot the ‘normal_transports’ variable.
plt.figure()
cross_transport_mean = tran_f.data_cross_tran_flow.normal_transports.mean(dim="t_dim")
cross_transport_mean.rolling(r_dim=2).mean().plot()
plt.ylabel("Sv")
plt.show()
Feedback
Was this page helpful?
Glad to hear it!
Sorry to hear that. Please tell us how we can improve.