Altimetry tutorial
Altimetry tutorial example.
4 minute read
This is a demonstration script for using the Altimetry object in the COAsT package. This object has strict data formatting requirements, which are outlined in altimetry.py.
Relevant imports and filepath configuration
# Begin by importing coast and other packages
import coast
root = "./"
# And by defining some file paths
dn_files = root + "./example_files/"
fn_nemo_dat = dn_files + "coast_example_nemo_data.nc"
fn_nemo_dom = dn_files + "coast_example_nemo_domain.nc"
fn_nemo_config = root + "./config/example_nemo_grid_t.json"
fn_altimetry = dn_files + "coast_example_altimetry_data.nc"
fn_altimetry_config = root + "./config/example_altimetry.json"
/usr/share/miniconda/envs/coast/lib/python3.10/site-packages/pydap/lib.py:5: DeprecationWarning: pkg_resources is deprecated as an API. See https://setuptools.pypa.io/en/latest/pkg_resources.html
/usr/share/miniconda/envs/coast/lib/python3.10/site-packages/pkg_resources/__init__.py:2871: DeprecationWarning: Deprecated call to `pkg_resources.declare_namespace('pydap')`.
Implementing implicit namespace packages (as specified in PEP 420) is preferred to `pkg_resources.declare_namespace`. See https://setuptools.pypa.io/en/latest/references/keywords.html#keyword-namespace-packages
/usr/share/miniconda/envs/coast/lib/python3.10/site-packages/pkg_resources/__init__.py:2871: DeprecationWarning: Deprecated call to `pkg_resources.declare_namespace('pydap.responses')`.
Implementing implicit namespace packages (as specified in PEP 420) is preferred to `pkg_resources.declare_namespace`. See https://setuptools.pypa.io/en/latest/references/keywords.html#keyword-namespace-packages
/usr/share/miniconda/envs/coast/lib/python3.10/site-packages/pkg_resources/__init__.py:2350: DeprecationWarning: Deprecated call to `pkg_resources.declare_namespace('pydap')`.
Implementing implicit namespace packages (as specified in PEP 420) is preferred to `pkg_resources.declare_namespace`. See https://setuptools.pypa.io/en/latest/references/keywords.html#keyword-namespace-packages
/usr/share/miniconda/envs/coast/lib/python3.10/site-packages/pkg_resources/__init__.py:2871: DeprecationWarning: Deprecated call to `pkg_resources.declare_namespace('pydap.handlers')`.
Implementing implicit namespace packages (as specified in PEP 420) is preferred to `pkg_resources.declare_namespace`. See https://setuptools.pypa.io/en/latest/references/keywords.html#keyword-namespace-packages
/usr/share/miniconda/envs/coast/lib/python3.10/site-packages/pkg_resources/__init__.py:2350: DeprecationWarning: Deprecated call to `pkg_resources.declare_namespace('pydap')`.
Implementing implicit namespace packages (as specified in PEP 420) is preferred to `pkg_resources.declare_namespace`. See https://setuptools.pypa.io/en/latest/references/keywords.html#keyword-namespace-packages
/usr/share/miniconda/envs/coast/lib/python3.10/site-packages/pkg_resources/__init__.py:2871: DeprecationWarning: Deprecated call to `pkg_resources.declare_namespace('pydap.tests')`.
Implementing implicit namespace packages (as specified in PEP 420) is preferred to `pkg_resources.declare_namespace`. See https://setuptools.pypa.io/en/latest/references/keywords.html#keyword-namespace-packages
/usr/share/miniconda/envs/coast/lib/python3.10/site-packages/pkg_resources/__init__.py:2350: DeprecationWarning: Deprecated call to `pkg_resources.declare_namespace('pydap')`.
Implementing implicit namespace packages (as specified in PEP 420) is preferred to `pkg_resources.declare_namespace`. See https://setuptools.pypa.io/en/latest/references/keywords.html#keyword-namespace-packages
/usr/share/miniconda/envs/coast/lib/python3.10/site-packages/pkg_resources/__init__.py:2871: DeprecationWarning: Deprecated call to `pkg_resources.declare_namespace('sphinxcontrib')`.
Implementing implicit namespace packages (as specified in PEP 420) is preferred to `pkg_resources.declare_namespace`. See https://setuptools.pypa.io/en/latest/references/keywords.html#keyword-namespace-packages
Load data
# We need to load in a NEMO object for doing NEMO things.
nemo = coast.Gridded(fn_nemo_dat, fn_nemo_dom, config=fn_nemo_config)
# And now we can load in our Altimetry data. By default, Altimetry is set up
# to read in CMEMS netCDF files. However, if no path is supplied, then the
# object's dataset will be initialised as None. Custom data can then be loaded
# if desired, as long as it follows the data formatting for Altimetry.
# altimetry = coast.Altimetry(fn_altimetry)
altimetry = coast.Altimetry(fn_altimetry, config=fn_altimetry_config)
/usr/share/miniconda/envs/coast/lib/python3.10/site-packages/xarray/core/dataset.py:282: UserWarning: The specified chunks separate the stored chunks along dimension "time_counter" starting at index 2. This could degrade performance. Instead, consider rechunking after loading.
././config/example_altimetry.json
Altimetry object at 0x562b801a3980 initialised
/usr/share/miniconda/envs/coast/lib/python3.10/site-packages/xarray/core/dataset.py:282: UserWarning: The specified chunks separate the stored chunks along dimension "time" starting at index 1000. This could degrade performance. Instead, consider rechunking after loading.
Subsetting
# Before going any further, lets just cut out the bit of the altimetry that
# is over the model domain. This can be done using `subset_indices_lonlat_box`
# to find relevant indices and then `isel` to extract them. The data here is then also
# also thinned slightly.
ind = altimetry.subset_indices_lonlat_box([-10, 10], [45, 60])
ind = ind[::4]
altimetry = altimetry.isel(t_dim=ind)
Subsetting Altimetry object at 0x562b801a3980 indices in [-10, 10], [45, 60]
Model interpolation
# Before comparing our observations to the model, we will interpolate a model
# variable to the same time and geographical space as the altimetry. This is
# done using the obs_operator() method:
altimetry.obs_operator(nemo, mod_var_name="ssh", time_interp="nearest")
# Doing this has created a new interpolated variable called interp_ssh and
# saved it back into our Altimetry object. Take a look at altimetry.dataset
# to see for yourself.
Interpolating Gridded object at 0x562b801a3980 "ssh" with time_interp "nearest"
#altimetry.dataset # uncomment to print data object summary
Interpolated vs observed
# Next we will compare this interpolated variable to an observed variable
# using some basic metrics. The basic_stats() routine can be used for this,
# which calculates some simple metrics including differences, RMSE and
# correlations. NOTE: This may not be a wise choice of variables.
stats = altimetry.basic_stats("ocean_tide_standard_name", "interp_ssh")
Altimetry object at 0x562b801a3980 initialised
# Take a look inside stats.dataset to see all of the new variables. When using
# basic stats, the returned object is also an Altimetry object, so all of the
# same methods can be applied. Alternatively, if you want to save the new
# metrics to the original altimetry object, set 'create_new_object = False'.
#stats.dataset # uncomment to print data object summary
# Now we will do a more complex comparison using the Continuous Ranked
# Probability Score (CRPS). For this, we need to hand over the model object,
# a model variable and an observed variable. We also give it a neighbourhood
# radius in km (nh_radius).
crps = altimetry.crps(nemo, model_var_name="ssh", obs_var_name="ocean_tide_standard_name", nh_radius=20)
# Again, take a look inside `crps.dataset` to see some new variables. Similarly
# to basic_stats, `create_new_object` keyword arg can be set to `false` to save output to
# the original altimetry object.
#crps.dataset # uncomment to print data object summary
Altimetry object at 0x562b801a3980 initialised
Plotting data
# Altimetry has a ready built quick_plot() routine for taking a look at any
# of the observed or derived quantities above. So to take a look at the
# 'ocean_tide_standard_name' variable:
fig, ax = altimetry.quick_plot("ocean_tide_standard_name")
/usr/share/miniconda/envs/coast/lib/python3.10/site-packages/cartopy/io/__init__.py:241: DownloadWarning: Downloading: https://naturalearth.s3.amazonaws.com/50m_physical/ne_50m_coastline.zip
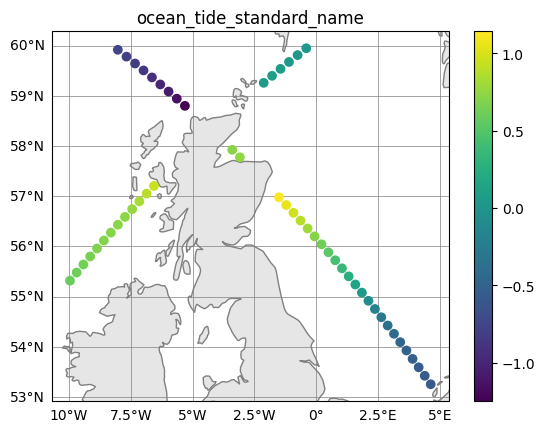
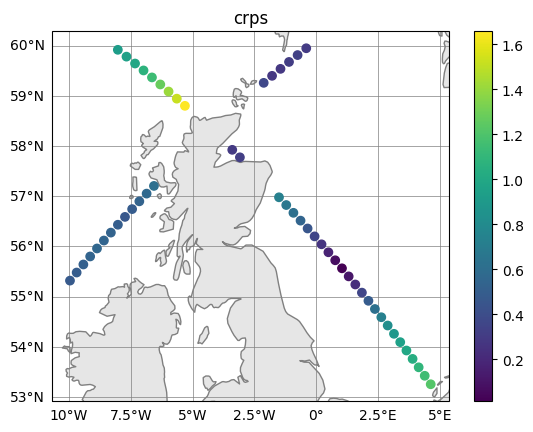
# As stats and crps are also `altimetry` objects, quick_plot() can also be used:
fig, ax = crps.quick_plot("crps")
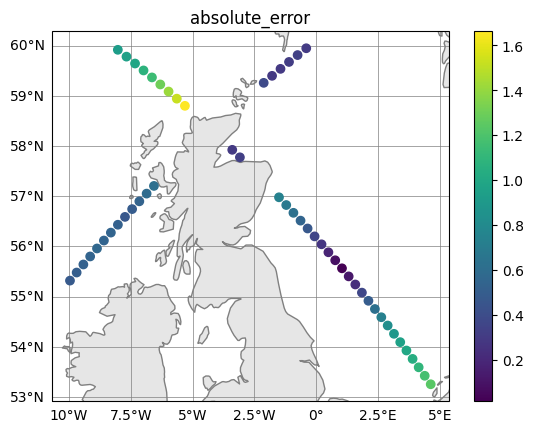
# stats quick_plot:
fig, ax = stats.quick_plot("absolute_error")
Feedback
Was this page helpful?
Glad to hear it!
Sorry to hear that. Please tell us how we can improve.
Last modified December 11, 2023: Updated Altimetry notebook pages from coast repo. (a2f146b)